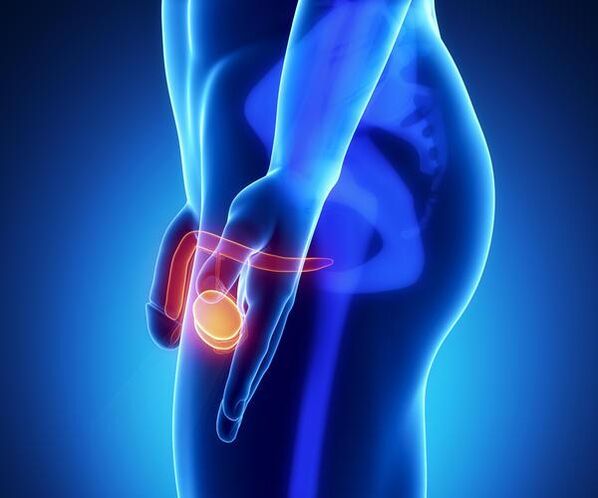
The health of the organs of the male reproductive system depends on many factors. Deviations in their functioning can be caused not only by internal malfunctions, but also by mechanical damage. The most vulnerable testicles are paired glands that produce male hormones and sperm. When injured, the ability to produce these substances is impaired, which affects not only sexual performance and the ability to fertilize, but also general health.
Main functions of the testicles
The testicles, also called testicles or testicles, are the male sex glands. Each of them is located in the scrotum - its right and left parts. The testicles are attached to the spermatic cords, which are made up of muscles, nerves, lymphatic vessels, and blood vessels. The right testicle is slightly higher than the left.
The testes are made of soft tissue divided into peculiar lobules by a thin connective septum. In them are the seminiferous tubules, in which sperm production takes place, and between them the process of production of the hormone testosterone takes place.
The constant formation of male germ cells enables the process of fertilization of the egg cell. The production of testosterone in the testicles is also very important for male health, because this hormone is responsible for the growth of the body and muscles, the development of the body as a whole according to the male type and the formation of sex hormones desire.
If the testicles are damaged for any reason, the ability to produce hormones and sex cells is reduced. This can happen at any age. In order to avoid complications, if you experience pain in the testicles, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Why do testicles hurt?
The causes of testicular pain in men are numerous. They can be both relatively harmless, associated with erroneous ejaculation after arousal, and dangerous, as they are a consequence of the development of malignant tumors or trauma to the external genital organs.
The reasons why the testicles hurt are as follows:
- Injury to the perineum or scrotum. If the blow or bruise was not too intense, the pain in the testicle is sharp, but passes quickly enough. At the same time, even a slight mechanical impact contributes to bleeding into the scrotal cavity, causing the skin to redden and thicken. Such phenomena pass in a few days. With a serious injury, the integrity of the testicles is violated. The pain in this case is so pronounced and painful that the victim can lose consciousness. A serious injury can lead to the fact that the gonad completely loses its functions - in the future this is fraught with infertility;
- Inflammatory processes in the testicles or their appendages. This can be epididymitis caused by the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms into the epididymis. In this case, the patient complains not only of pain, but also of swollen testicles. The pathological process can also occur as a result of inflammation of the glandular tissue. This phenomenon is called orchitis. This disease, which is a complication of influenza, gonorrhea, and others, can affect one or both testicles at the same time, causing infertility. With orchitis, the skin of the testicles turns red, the scrotum swells, the man has a fever, there is general weakness and constant thirst;
- Abstinence. In this case, men experience pulling pains in the testicles, because when excited, the penis fills with blood and the duct system is activated - all this indicates readiness for ejaculation. If this does not happen, then unpleasant sensations appear in the testicles. Unlike cases when pain is caused by pathological processes, discomfort in the testicles during prolonged abstinence is not accompanied by general weakness, loss of appetite, dizziness, and changes in the color of urine. This problem does not need to be treated, it can be solved either through sexual intercourse or through masturbation. Another way to get rid of discomfort is to take a painkiller;
- Frequent interruptions in sexual intercourse or lack of ejaculation after prolonged excitement, neurological pathologies and inflammatory diseases of the digestive system - all these factors can explain why the testicles hurt after sex;
- Varicocele is a pathological expansion of the veins and vessels of the penis due to their insufficiency. This disease is often encountered by adolescents of adolescence. If the testicle hurts precisely for this reason, then the disease is in an advanced stage, and this is fraught with amputation of the organ. Also, varicocele is accompanied by an enlargement of one of the halves of the scrotum;
- hernia. When injured, acute pain is observed, a specific protrusion in the groin, which increases with physical exertion and, after taking a horizontal position, acquires its former form. If the injury to the contents of the hernia does not occur, then there is a dull pain radiating to the abdomen, side, lower limb area;
- hydrocele or hydrocele. This phenomenon is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the membranes of the testicles, which is accompanied by impaired blood flow. The disease can be hereditary or appear with inflammatory diseases, the development of tumors, after injuries to the external genital organs. If the testicle has enlarged, the presence of a hydrocele can be suspected. Another symptom characteristic of this pathology is a sharp pain that occurs when touching the testicles;
- testicular torsion. This phenomenon usually occurs in boys aged 7-10 years and is characterized by twisting of the spermatic cord, resulting in blockage of local blood flow and crushing of the duct. Pain in this case occurs only in one of the testicles. Unpleasant sensations are aggravated by walking or pressing on the affected area. There may be redness in the scrotum and an increase in one of its sides, as well as a burning sensation. Such a deviation is corrected either by external reduction of the testicle or by surgical methods;
- The development of a malignant tumor. The pathological process can spread to both the glandular tissue and the excretory ducts. In this case, the testicles in men hurt only when the neoplasm has grown large;
- inflammation of the prostate. If the testicles hurt during prostatitis, this is one of the leading symptoms of the disease.
- In men, inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs cause pain in the lower abdomen and testicles;
- hypothermia. The result of exposure to low temperatures can be aching testicle pain in men. In some cases, there is an increase in body temperature.
If a man notices pain in the testicles, as well as external changes - an increase in their size, redness, swelling - you should immediately consult a doctor in order to determine the cause of the pathological manifestations as soon as possible and start appropriate treatment.
Characteristic features of pain
When making a diagnosis, the type of pain that occurs in the region of the testicles is of great importance. Depending on where it radiates, preliminary conclusions can be drawn about the nature of the appearance of unpleasant sensations.
- In the event that the pain radiates to the lumbar region or abdomen, the presence of an inflammatory process occurring in the epididymis is suspected;
- If the pain radiates to the side, urolithiasis or hernia may occur;
- If the pain radiates to the lower extremity, suspect a torsion of the spermatic cord or a testicular contusion with subsequent bleeding in the testicles.
If the testicles are red and feel pain and discomfort in them, then it is urgent to undergo the diagnostic measures prescribed by the doctor. Delay in this case can lead to infertility due to the lack of motile sperm in the ejaculate, impaired potency or penile amputation.
diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of cases when the testicle hurts and pulls is made by a urologist and andrologist. A man must go through the following activities:
- A general blood test, thanks to which a specialist can identify the inflammatory process;
- Sperm analysis for infections to determine the presence and type of pathogenic microorganisms;
- Analysis of the spermiogram, which allows you to evaluate the activity of sperm and identify bacteria;
- Ultrasound of the scrotum, which allows you to identify tumor neoplasms;
- Taking a swab from the urethra to identify pathogens;
- Puncture (puncture biopsy) to determine the nature of diseases of the testicles, appendages;
- palpation to detect tumors or enlargement of the testicles;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and ureters to detect formations that impede the flow of urine;
- CT and MRI to rule out a misdiagnosis.
Before conducting diagnostic measures, the patient is not recommended to take painkillers, conduct warming or cooling procedures.
treatment methods
Treatment for pain in the testicles depends on what is causing the discomfort. Therapy can be based on drugs, special procedures, or surgery.
Table 1. Methods of treating testicular pain
| because | treatment |
| Slight bruising of the vulva |
|
| Infectious diseases caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the scrotum organs |
|
| varicocele |
|
| tumor | Removal of the tumor by radiation therapy or removal of the affected organ by surgery. If metastases are detected, chemotherapy is required. |
| testicular torsion | Dissection of the scrotum, assessment of the viability of the testicle and its subsequent straightening or removal. In the postoperative period, the use of painkillers is indicated. |
| Extensive hematomas | Drainage of affected areas, removal of non-viable tissue and suturing of gaps. |
It is not recommended to use folk remedies to eliminate pain in the scrotum, since such an alarming symptom requires careful diagnosis. However, there are some steps you can take while you wait to see the doctor to relieve the discomfort caused by a light blow or bruise. At home, you can put an ice pack on the sore side or do a light massage with an anesthetic cream, but it is better not to touch the affected area until you consult a specialist.
To prevent the onset of pain in such a vulnerable organ as the testicles, you should:
- timely eliminate anomalies in the structure of the genital organs;
- Be regularly examined by a urologist to identify pathologies that are asymptomatic in the early stages of development;
- Have a regular sex life and use barrier contraceptives if partner is unstable;
- Wear underwear that does not compress organs and does not affect blood flow.
- normalize drinking regime and nutrition;
- Prevent the possibility of a traumatic impact on the scrotum.
The condition of the testicles not only directly affects a man's reproductive ability, but also his overall health. In order to avoid undesirable consequences, it is necessary to minimize the risk of external factors affecting the testicles and timely treat existing diseases that can adversely affect their condition.